1. Type of Raw Materials
Curtain Material:

Common soft curtain materials include PVC fabric, inorganic cloth, and mesh curtains, which are relatively low-cost. In contrast, rigid curtain materials such as aluminum alloy slats, stainless steel panels, and color-coated sandwich panels are heavier and stronger, thus more expensive. For example, rigid high-speed doors often use double-layer 0.7mm aluminum alloy with polyurethane insulation (total thickness approx. 4–5 cm), while PVC high-speed doors are typically made of 0.9–2.5 mm single-layer fabric. The former has significantly higher material costs and is suitable for wind resistance and insulation purposes.
Door Structure:
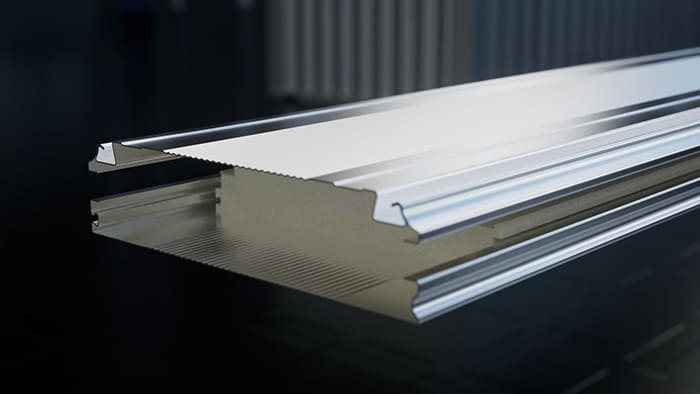
Door frames and tracks are commonly made of hot-dip galvanized steel or aluminum profiles. The more robust the structure—such as thickened steel frames, double-layer panels, or reinforced springs—the higher the cost. For instance, Fastlink's HSV-HAS series Sprial high speed doors use high quality aluminum panels for excellent insulation and durability, resulting in higher costs.
Sealing Materials:
High-quality sealing components, such as EPDM rubber strips or elastic brushes, significantly improve airtightness and insulation but also increase cost. Rigid high-speed doors generally use rubber seals for better insulation, while soft PVC doors often use a combination of brush and rubber strips. Advanced sealing solutions (e.g., soft bottom edge with safety sensors) enhance safety and comfort but also increase expenses.
2. Size and Customization
 Door Dimensions:
Door Dimensions:
The size (width × height) directly affects material usage and production cost. Larger doors require more materials and thicker panels or slats, which further increases the unit price.
Customization Requirements:
Non-standard sizes or special designs—such as curved doors or side-sliding tracks—require additional engineering and production costs. Custom features like unique colors, printed logos, or anti-static coatings also add to the price. Generally, the more non-standard the specification, the higher the cost.
Installation Type:
Different installation styles—recessed, wall-mounted, vertical, or lateral rolling—may require specific components and installation techniques, affecting the final price.
3. Control System Configuration
Motor and Drive System:

The power and brand of the motor greatly impact cost. For example, Fastlink uses servo motor that are more expensive but offer better reliability and longer service life than common motor. Using an inverter (for adjustable speed) is costlier than direct drive, but enables smoother high-frequency operation.
Control Method:
Basic control panels with simple limit switches are the most economical. Advanced systems featuring PLCs, inverters, touchscreen interfaces, and HMIs are significantly more expensive.
Sensors and Detectors:
Adding ground loops, radar/ microwave sensors, infrared beams, or photoelectric detectors enables contactless automatic operation, increasing system costs. Entry-level models are usually sensor-free, while high-end models equipped with radar and photoelectric sensors are significantly pricier.
4. Safety Control Devices
Safety Light Curtains or Grids:
Installed on both sides or at the top of the door opening, these infrared barriers detect obstructions in real-time to ensure safe closing. While increasing system cost, they effectively prevent accidents.
Photoelectric Sensors:
Installed at the bottom or on the door panel, these devices detect obstacles and trigger automatic stopping or reversing. They add to the hardware cost.
Soft Bottom Edge / Pressure Strip:
A flexible strip or pressure-sensitive device at the curtain bottom allows the door to rebound upon detecting impact. These not only improve sealing but also enhance safety, with higher production costs than standard hard bottom edges.
Other Devices:
Emergency stop buttons, collision buffers, and braking systems also add to the cost. Overall, the more comprehensive the safety configuration, the higher the system cost.
5. Opening Frequency and Operating Speed
High-Frequency Operation:
In environments with frequent usage, such as automotive assembly lines or logistics centers, doors must endure high cycle counts. This requires durable components such as long-life springs, high-quality bearings, and high-speed motors, leading to higher costs.
Operating Speed:
High-speed doors generally open faster than conventional doors (e.g., up to 2 m/s or more). Fast opening requires stronger motors and stable control systems to ensure performance and longevity. For instance, Fastlink’s high-performance motor and control system are rigorously tested to maintain stability under high-frequency operation. Higher speed and frequency demand higher standards in structure and drive system, thereby increasing cost.
6. Brand and Manufacturer Services
 Brand Premium:
Brand Premium:
Well-known brands or international manufacturers often target the high-end market with better product performance and reliability, resulting in higher pricing. Brand-related factors include R&D investment, quality certifications, and market positioning. Lesser-known brands may offer lower prices, but differences in performance and after-sales service exist.
Warranty and Service:
The length and quality of warranty and after-sales service directly affect pricing. Premium brands usually offer warranties of over one year, along with professional installation and maintenance. Fastlink takes the lead in investing resources to establish an intelligent service management platform, and continuously launches service functions such as efficient inquiry of orders for customers and one-click report for repair and customer evaluation on the mobile phone, to realize end-to-end service that starts with customer demand and ends with customer satisfaction
Installation and Commissioning:
Some suppliers include free or paid installation and commissioning services in their packages. More comprehensive service offerings (e.g., 24-hour response, routine maintenance) are reflected in higher prices.
6. Transportation and Installation Costs
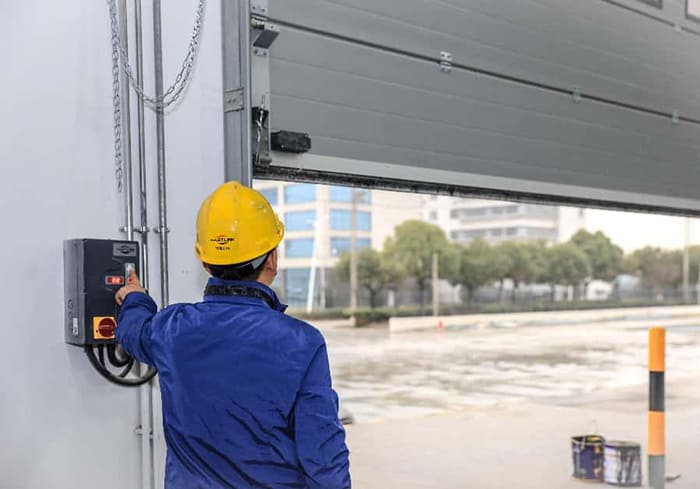 Transportation Fees:
Transportation Fees:
Large door systems are bulky and heavy, requiring specialized logistics and insurance for long-distance or cross-border transport. The farther the destination and the more complex the road conditions, the higher the costs. It is noted that "installation complexity and distance affect installation costs.”
Installation Difficulty:
Challenging environments—such as high-rise installations, bad weather, or unique structural conditions—require more manpower, equipment, or reinforcement, increasing labor costs.
Additional Fees:
Turnkey service packages that include commissioning and acceptance testing are generally priced higher than material-only quotations. Combined transportation and installation costs can account for 10–20% of the total door system price.
Industrial door pricing hinges on material durability, automation demands, and operational intensity, shaped collectively by technical specifications and service value chains. Strategic procurement balances performance needs with lifecycle cost considerations. As a provider of advanced intelligent solutions for access points, Fastlink offers personalized high-end customization tailored to your needs, dedicated to delivering high-quality products and satisfactory prices.







